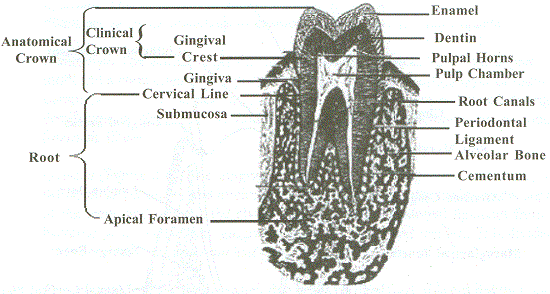
The Human tooth is something you cannot see as a whole directly, as half of it is embedded in the jaw bone and the small structure has got several parts, each providing a specific purpose and the tooth is divided into two main areas – Crown and Root. Crown is the portion that can be seen directly to the eye, while the root is a part that is not visible, but can be one of the reasons for several problems in the tooth, as it has the path for the blood vessels and nerves.
Unlike the crown, the root part has got a very thin layering and its diameter is too less and most of the roots are tapering and not more than mm in thickness at its tip. Below is the brief summary of what all parts a Human tooth comprises of.
Enamel: This is the hardest substance in the body, giving the strength to the tooth to bite through all the food that is consumed by the person. Although being very strong, it cannot handle the bacterial acid production, and gets dissolved due to the acids that are produced due to plaque formation. Enamel is seen only in the crown part of the tooth, which is visible in the mouth.
Dentin: This is the layer that lies just inside the enamel, and it is not as hard as the enamel but is flexible and holds the strength which is similar to that of the bone. This is the layer that handles and distributes the load to the other parts of the tooth when a hard substance is bitten.
Pulp: It is the soft tissue occupying the central cavity of a tooth, thus is the innermost layer of the tooth. This is the part of the tooth, which provides all the nutrition to the other parts, and is a house for all the nerves inside the tooth. Pulp cavity is the central cavity in a tooth which contains dental pulp. Pulp chamber is that portion of the pulp cavity which lies in the crown of tooth. Pulp horns are extensions of pulp chamber towards occlusal or incisal surface. Pulpal walls are sides of pulp chamber. Pulp Canal or root canal is that portion of pulp cavity which lies in the root portion of tooth.
Cementum: This is a thin layer that lies over the dentin in the root portion of the tooth. It is the part that provides the attachment between the tooth and the bone through the periodontal ligament.
Clinical parts / structures of a human tooth:

- Crown: A clinical crown is that portion of tooth which is visible in mouth. Anatomical crown is that portion of tooth which is covered by enamel.
- Crypt is a cavity in the alveolar bone that contains developing tooth germ of a permanent tooth.
- Cusp is an elevated point on the crown portion of the tooth. A cusp has four ridges and an apex.
- Embrasure is the space adjacent to contact point, e.g. buccal embrasure, gingival embrasure, lingual embrasure and occlusal embrasure.
- Fissure: A fissure is a defect on the surface of a tooth due to faulty joining of the enamel of different lobes.
- Fossa is a rounded depression on the surface of a tooth. It occurs commonly on occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth and lingual surfaces of anterior teeth. Occlusal fossae may be either central or triangular.
- Groove: A groove is a linear depression that is seen on the surface of the tooth. It is different from a developmental groove, which denotes the point of coalescence between the primary parts of the crown or root. It may be buccal or lingual and are seen on buccal and lingual surfaces of posterior teeth.
- Ridge is represented by long, elevated ports on the tooth surface. There are different ridges, namely buccal, incisal, and marginal ridge depending on their locations. Marginal ridges are rounded elevations of enamel that forms the mesial and distal margins of the occlusal surfaces of the posterior teeth and lingual surfaces of the anterior teeth.
- Triangular ridges are those ridges which descend from the tips of cusps of posterior teeth towards centre of occlusal surfaces. Each triangular ridge has a triangular shaped slope or inclined plane on each side. A Transverse ridge is formed by the union of a buccal and a lingual triangular ridge on the occlusal surfaces of the posterior teeth and runs transversely. An oblique ridge is also formed by junction of two triangular ridges but runs obliquely across the occlusal surfaces of upper molars.
- Sulcus is a long depression on the surface of a tooth, the inclines of which meet at an angle.
- Trunk is the main body of the root of multi-rooted tooth, from the cervical line till its division.
- Tubercle is a small rounded elevation of enamel on the crown of a tooth.
very helpful! thank you 🙂