Motor Nerve
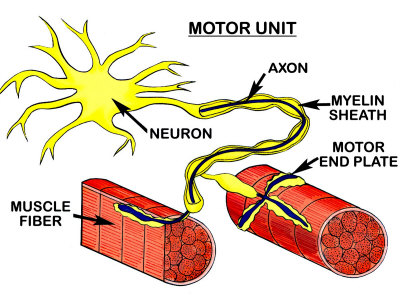
Impulses form the central nervous system, which are responsible for triggering muscle contraction, are carried by a nerve called a motor nerve. Motor nerves control every voluntary muscle in the body. Thus, a motor nerve is involved whenever some decides to make a movement. To control their voluntary muscles, this highly effective system is used by every vertebrate animal. On the other hand, a different system is used to move involuntary muscles like the heart. Neurons known as motor neurons specializing to carry signals that result in muscle contraction make up these motor nerves. Muscle contraction is stimulated by chemicals that are released by a motor neuron when a motor nerve meets a muscle. The muscle again relaxes once these chemicals break down. Motor nerves can also cause muscles to contract but cannot relax them, thus they merely having an excitatory action.
Motor Neuron
The contraction or relaxation of muscles is directly or indirectly controlled be a type of cell in the nervous system that is known as a motor neuron. While controlling the contraction or relaxation of muscles, motor neurons also lead to body movement as well. Motor neurons can even be called motoneurons or efferent neurons. Information from the central nervous system is also carried by motor neurons to muscles and other systems. Due to having a unique design, a motor neuron is ideally able to service its purpose despite of being a cell. The dendrites, the cell body and the axon are the three parts composed in a motor neuron. It is from the cell body where motor neurons branch out and the electrochemical signals are received from other units of the nervous system.
Thus when it comes to muscle contraction or relaxation and body movements, motor nerves and neurons have their own individual functions.
Leave a Reply