It is a band of epithelium that has invaded the underlying ectomesenchyme along each of the horse shoe shaped dental arches. Dental lamina serve as primordium for deciduous teeth. It is the first formed part during the tooth development.
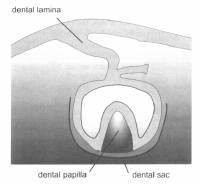
2-3 weeks after the rupture of the bucopharyngeal membrane, age of embryo being 6 weeks old, certain basal cells proliferate more rapidly and this leads to the formation of the dental lamina.
Permanent molars arise from the distal extension of the dental lamina.
The 1st permanent molar is initiated at 4th month in the utero.
The 2nd permanent molar is initiated at about 1st year after birth.
The 3rd permanent molar is initiated at about 4th-5th year after birth.
The successors of the deciduous teeth develop from a lingual extension of free end of dental lamina opposite to enamel organ of each deciduous tooth.
This lingual extension is called as Successional lamina and develops from 5th month in utero to 10th month of age.
Fate – DL’s total activity is about 5 years.
After it has disappeared everywhere, it still is present in the region of 3rd molar.
As the teeth continue to develop, they lose the connection with the dental lamina.
Remnants of dental lamina persist as epithelial pearls or islands within the jaw as well as in the gingiva.
excellent matter..it was so helpful for my representation in seminar…..iam very thnkful to u………thankyou so much………
nice info…very gud…thnks
THIS IS VERY GOOD DEFIEND THE DENTAL LAMINA IN THE SIMPLE LANGUAGE..
what are the remnants of dental lamina?
This is perfect defiend by dental lamina